EX-99.1
Published on October 10, 2025

ne mission. Advancing an inspired pipeline of novel IL-1β therapies focused on treating unmet medical needs. CORPORATE OVERVIEW OCTOBER 2025 | AVALO THERAPEUTICS, INC. (AVTX) Exhibit 99.1

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation may include forward-looking statements made pursuant to the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. Such forward-looking statements are subject to significant risks and uncertainties that are subject to change based on various factors (many of which are beyond Avalo’s control), which could cause actual results to differ from the forward-looking statements. Such statements may include, without limitation, statements with respect to Avalo’s plans, objectives, projections, expectations and intentions and other statements identified by words such as “projects,” “may,” “might,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “continue,” “seeks,” “aims,” “predicts,” “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “intends,” “plans,” “potential,” or similar expressions (including their use in the negative), or by discussions of future matters such as: integration of AVTX-009 into our operations; drug development costs, timing of trial results and other risks, including reliance on investigators and enrollment of patients in clinical trials; the intended use of the proceeds from the private placement; reliance on key personnel; regulatory risks; general economic and market risks and uncertainties, including those caused by the war in Ukraine and the Middle East; and those other risks detailed in Avalo’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, available at www.sec.gov. Actual results may differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. Except as required by applicable law, Avalo expressly disclaims any obligations or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in Avalo’s expectations with respect thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any statement is based. 2
Avalo Therapeutics: Advancing the Next-Generation of IL-1β Inhibition for Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases 3 IL, interleukin; IND, investigational new drug application; mAB, monoclonal antibody; MOA, mechanism of action. 1. Vossen ARJV, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(7):1463-1466.e2; 2. Kelly G, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(6):1431-1439; 3. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA; 4. Bihorel S, et al. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1009-1017; 5. HS Market Research 2024. Lead compound AVTX-009 (anti-IL-1β mAb) has the potential for best-in-class and best-in-disease profile in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) • Significant unmet need due to incomplete response and loss of response to current treatment • Abbvie’s lutikizumab (IL-1α/β) demonstrated favorable efficacy to market leaders and pipeline therapeutics in a refractory population that had failed anti-TNF therapy • IL-1β (not IL-1α) is a key immunoregulator in HS, based on preclinical and clinical evidence1,2,3 • AVTX-009 has 15x higher affinity and a longer half-life than lutikizumab, potentially predictive of higher efficacy and less frequent dosing4 Phase 2 LOTUS trial in HS enrolling with topline data expected mid-2026 HS market is expected to grow to > $10B by 20355 AVTX-009 has the potential to treat additional immune- mediated inflammatory diseases Expected cash runway into 2028

Avalo Management Team 4 A proven track record of successful leadership, product development, and commercialization in pharma and biotech Lisa Hegg, PhD SVP, Program Management, Business Development & Corporate Infrastructure Colleen Matkowski SVP, Global Regulatory Affairs, Quality Assurance Dino C. Miano, PhD SVP, CMC, Technical Operations Chris Sullivan Chief Financial Officer Mittie Doyle, MD Chief Medical Officer Paul Varki Chief Legal Officer Garry A. Neil, MD Chief Executive Officer Jennifer Riley Chief Strategy Officer 220+ Years of experience in biotech/pharmaAshley Ivanowicz SVP, Human Resources Taylor Boyd Chief Business Officer

AVTX-009: Designed to Target the Inflammatory Driver of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) to Address Significant Unmet Need 5
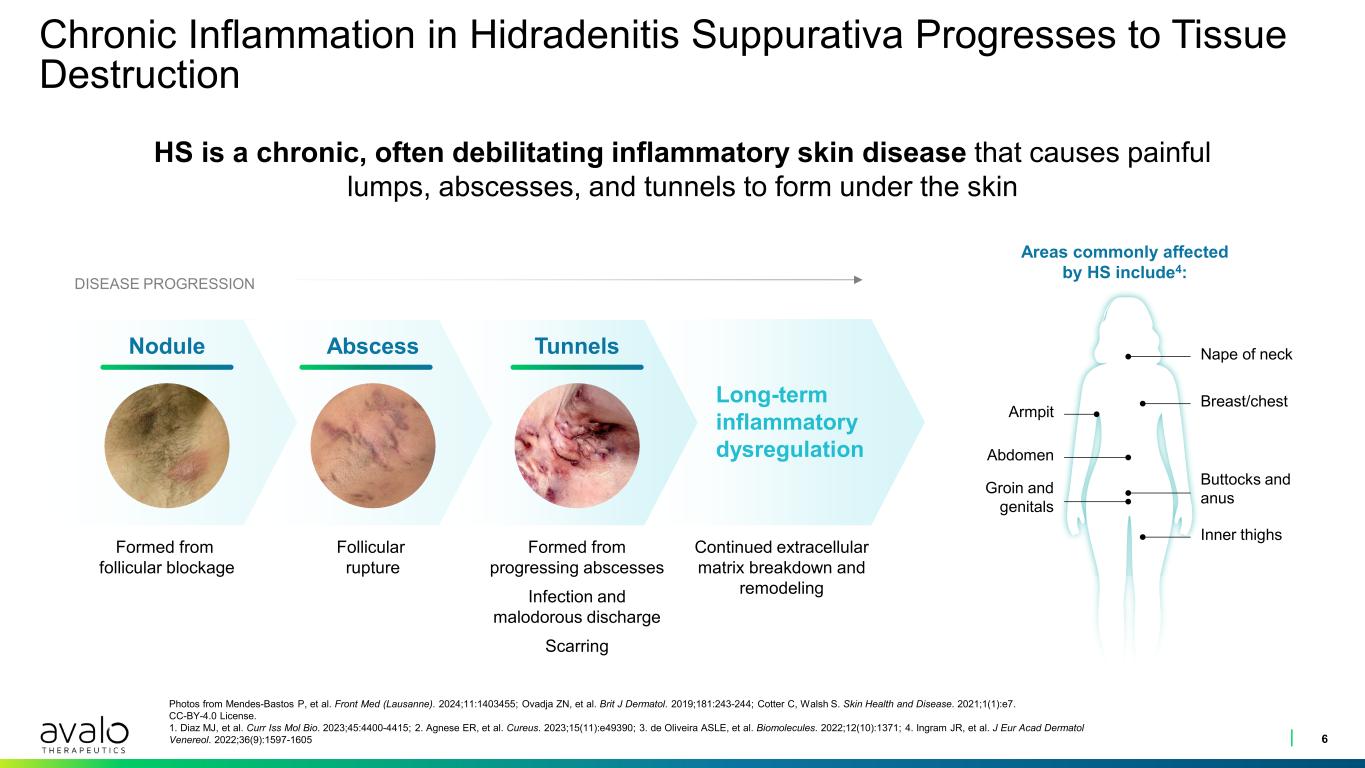
Chronic Inflammation in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Progresses to Tissue Destruction 6 Photos from Mendes-Bastos P, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1403455; Ovadja ZN, et al. Brit J Dermatol. 2019;181:243-244; Cotter C, Walsh S. Skin Health and Disease. 2021;1(1):e7. CC-BY-4.0 License. 1. Diaz MJ, et al. Curr Iss Mol Bio. 2023;45:4400-4415; 2. Agnese ER, et al. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e49390; 3. de Oliveira ASLE, et al. Biomolecules. 2022;12(10):1371; 4. Ingram JR, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(9):1597-1605 HS is a chronic, often debilitating inflammatory skin disease that causes painful lumps, abscesses, and tunnels to form under the skin Long-term inflammatory dysregulation Formed from progressing abscesses Infection and malodorous discharge Scarring Follicular rupture Formed from follicular blockage Areas commonly affected by HS include4: DISEASE PROGRESSION TunnelsAbscessNodule Nape of neck Breast/chest Buttocks and anus Inner thighs Groin and genitals Abdomen Armpit Continued extracellular matrix breakdown and remodeling
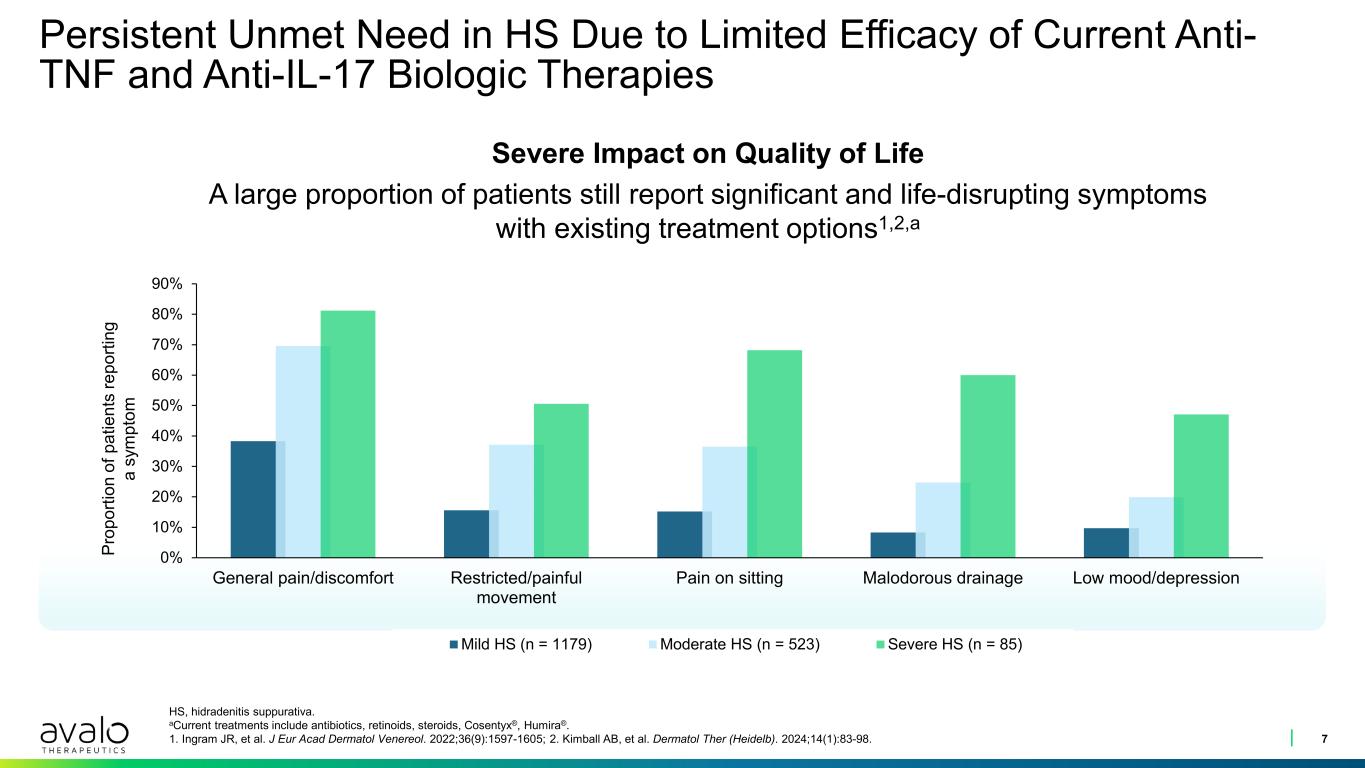
Persistent Unmet Need in HS Due to Limited Efficacy of Current Anti- TNF and Anti-IL-17 Biologic Therapies 7 HS, hidradenitis suppurativa. aCurrent treatments include antibiotics, retinoids, steroids, Cosentyx®, Humira®. 1. Ingram JR, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(9):1597-1605; 2. Kimball AB, et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14(1):83-98. 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% General pain/discomfort Restricted/painful movement Pain on sitting Malodorous drainage Low mood/depression Mild HS (n = 1179) Moderate HS (n = 523) Severe HS (n = 85) Severe Impact on Quality of Life A large proportion of patients still report significant and life-disrupting symptoms with existing treatment options1,2,a Pr op or tio n of p at ie nt s re po rti ng a sy m pt om
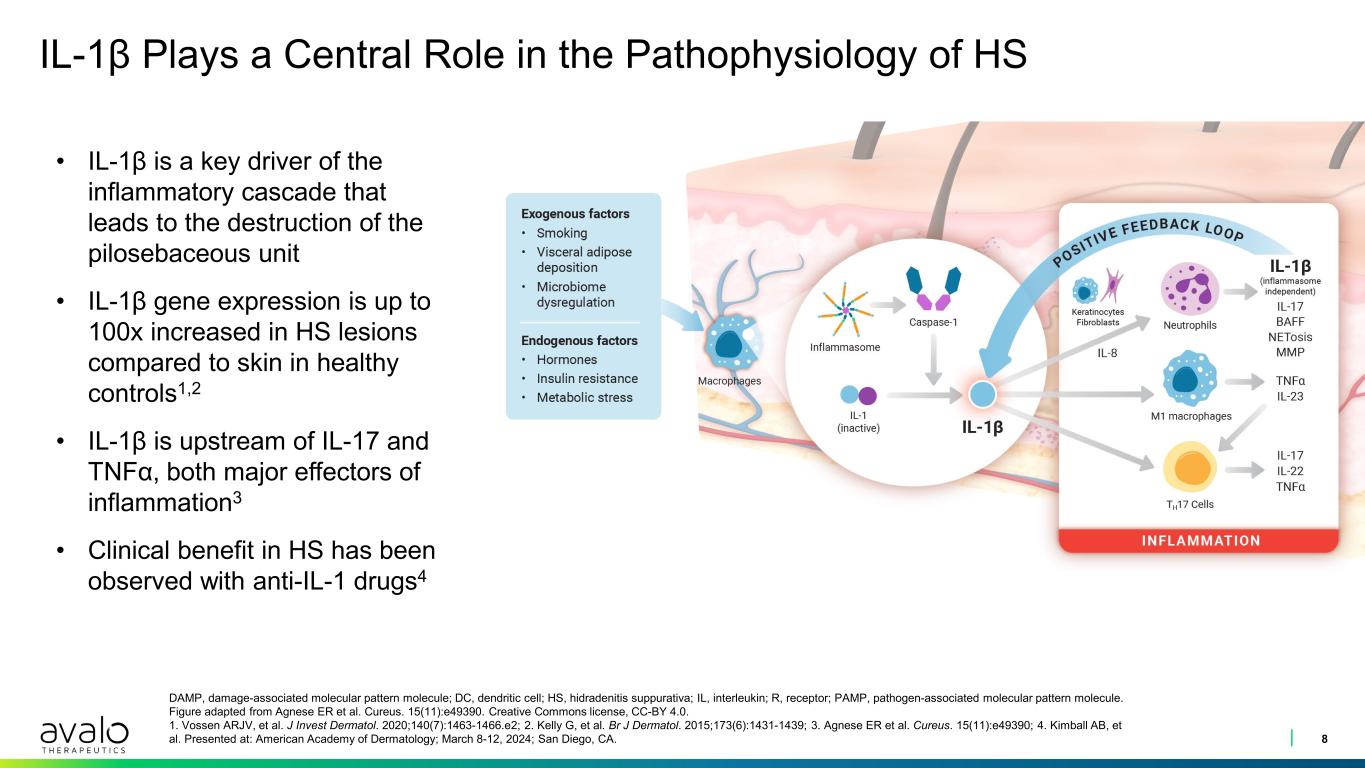
IL-1β Plays a Central Role in the Pathophysiology of HS 8 DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern molecule; DC, dendritic cell; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; IL, interleukin; R, receptor; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecule. Figure adapted from Agnese ER et al. Cureus. 15(11):e49390. Creative Commons license, CC-BY 4.0. 1. Vossen ARJV, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(7):1463-1466.e2; 2. Kelly G, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(6):1431-1439; 3. Agnese ER et al. Cureus. 15(11):e49390; 4. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA. • IL-1β is a key driver of the inflammatory cascade that leads to the destruction of the pilosebaceous unit • IL-1β gene expression is up to 100x increased in HS lesions compared to skin in healthy controls1,2 • IL-1β is upstream of IL-17 and TNFα, both major effectors of inflammation3 • Clinical benefit in HS has been observed with anti-IL-1 drugs4
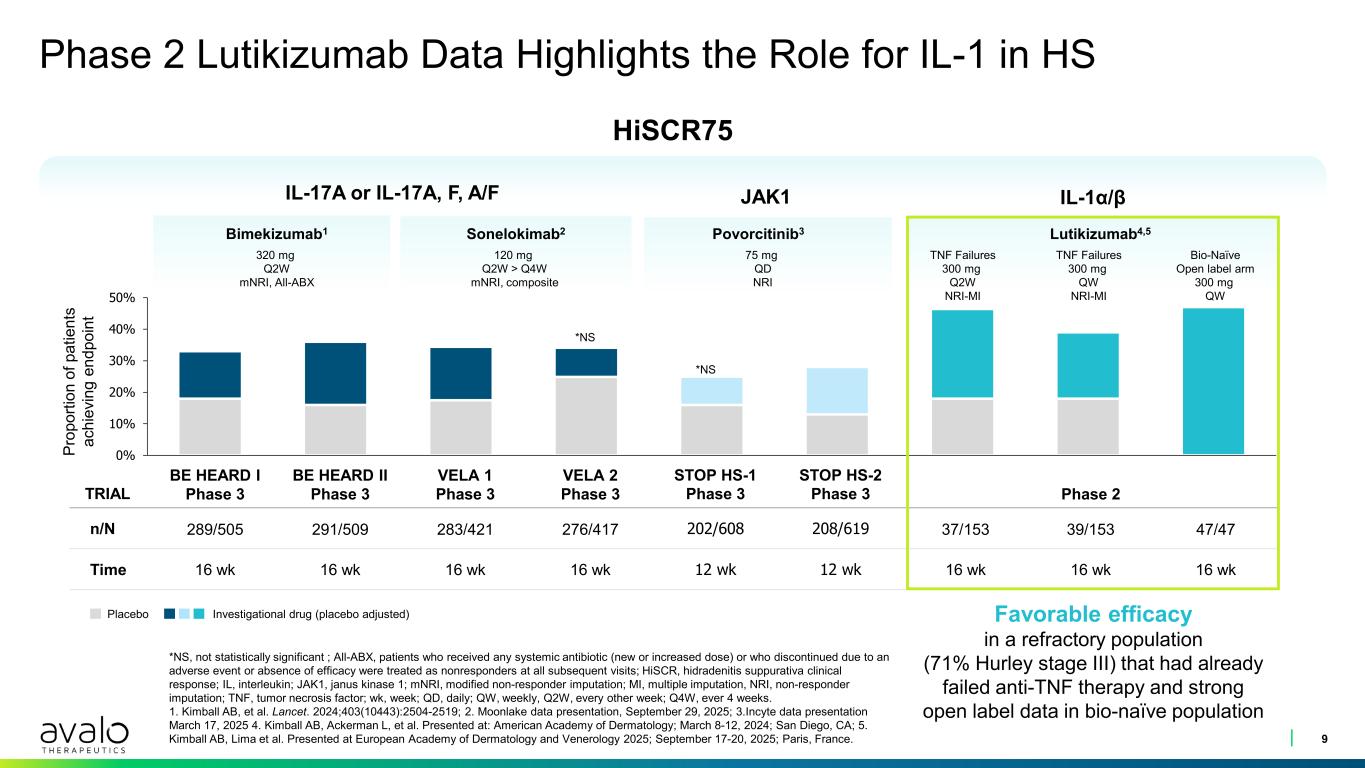
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Phase 2 Lutikizumab Data Highlights the Role for IL-1 in HS 9 *NS, not statistically significant ; All-ABX, patients who received any systemic antibiotic (new or increased dose) or who discontinued due to an adverse event or absence of efficacy were treated as nonresponders at all subsequent visits; HiSCR, hidradenitis suppurativa clinical response; IL, interleukin; JAK1, janus kinase 1; mNRI, modified non-responder imputation; MI, multiple imputation, NRI, non-responder imputation; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; wk, week; QD, daily; QW, weekly, Q2W, every other week; Q4W, ever 4 weeks. 1. Kimball AB, et al. Lancet. 2024;403(10443):2504-2519; 2. Moonlake data presentation, September 29, 2025; 3.Incyte data presentation March 17, 2025 4. Kimball AB, Ackerman L, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA; 5. Kimball AB, Lima et al. Presented at European Academy of Dermatology and Venerology 2025; September 17-20, 2025; Paris, France. TRIAL BE HEARD I Phase 3 BE HEARD II Phase 3 VELA 1 Phase 3 VELA 2 Phase 3 STOP HS-1 Phase 3 STOP HS-2 Phase 3 Phase 2 n/N 289/505 291/509 283/421 276/417 202/608 208/619 37/153 39/153 47/47 Time 16 wk 16 wk 16 wk 16 wk 12 wk 12 wk 16 wk 16 wk 16 wk IL-17A or IL-17A, F, A/F Sonelokimab2 120 mg Q2W > Q4W mNRI, composite Bimekizumab1 320 mg Q2W mNRI, All-ABX IL-1α/β Lutikizumab4,5 TNF Failures 300 mg Q2W NRI-MI TNF Failures 300 mg QW NRI-MI 75 mg QD *NS *NS HiSCR75 Pr op or tio n of p at ie nt s ac hi ev in g en dp oi nt Favorable efficacy in a refractory population (71% Hurley stage III) that had already failed anti-TNF therapy and strong open label data in bio-naïve population Placebo Investigational drug (placebo adjusted) JAK1 Povorcitinib3 75 mg QD NRI Bio-Naïve Open label arm 300 mg QW
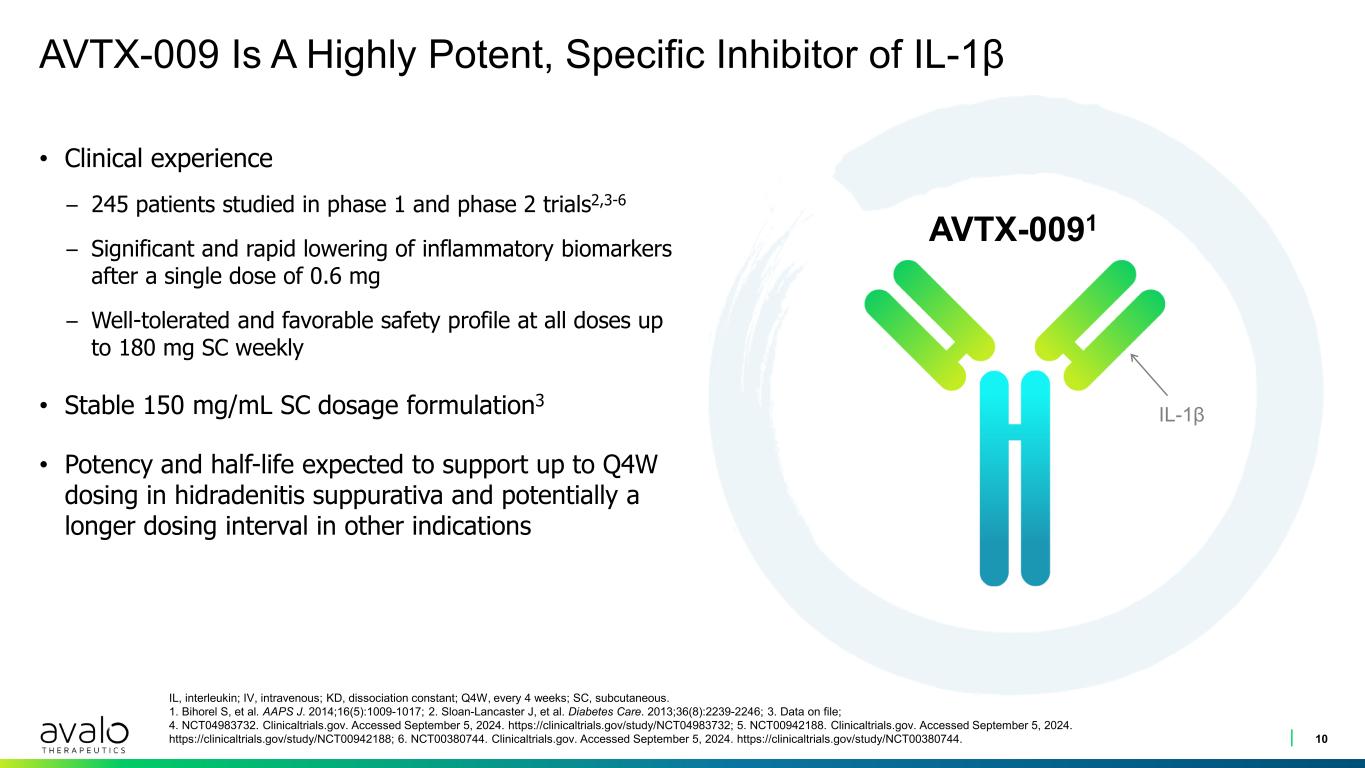
AVTX-009 Is A Highly Potent, Specific Inhibitor of IL-1β • Clinical experience – 245 patients studied in phase 1 and phase 2 trials2,3-6 – Significant and rapid lowering of inflammatory biomarkers after a single dose of 0.6 mg – Well-tolerated and favorable safety profile at all doses up to 180 mg SC weekly • Stable 150 mg/mL SC dosage formulation3 • Potency and half-life expected to support up to Q4W dosing in hidradenitis suppurativa and potentially a longer dosing interval in other indications 10 IL, interleukin; IV, intravenous; KD, dissociation constant; Q4W, every 4 weeks; SC, subcutaneous. 1. Bihorel S, et al. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1009-1017; 2. Sloan-Lancaster J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(8):2239-2246; 3. Data on file; 4. NCT04983732. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed September 5, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04983732; 5. NCT00942188. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed September 5, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00942188; 6. NCT00380744. Clinicaltrials.gov. Accessed September 5, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00380744. AVTX-0091 IL-1β
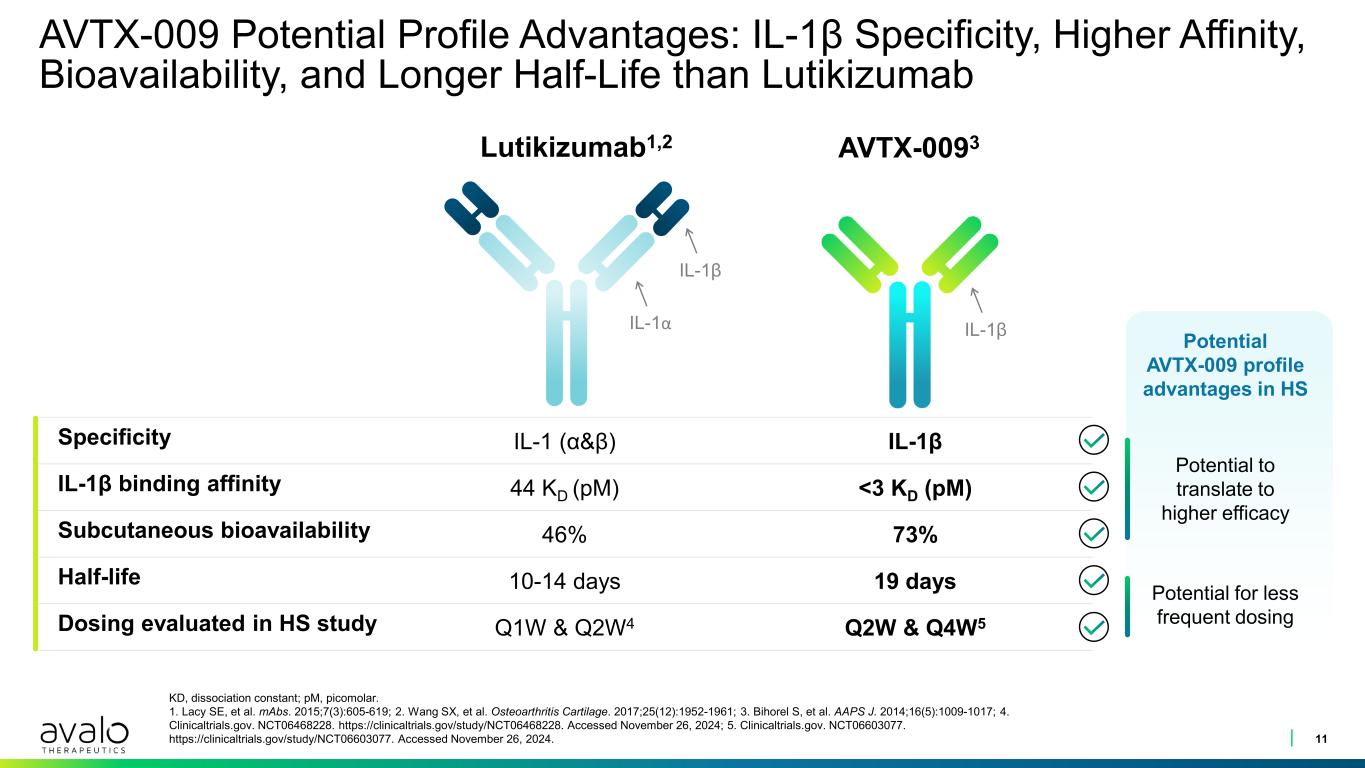
Specificity IL-1 (α&β) IL-1β IL-1β binding affinity 44 KD (pM) <3 KD (pM) Subcutaneous bioavailability 46% 73% Half-life 10-14 days 19 days Dosing evaluated in HS study Q1W & Q2W4 Q2W & Q4W5 AVTX-009 Potential Profile Advantages: IL-1β Specificity, Higher Affinity, Bioavailability, and Longer Half-Life than Lutikizumab 11 KD, dissociation constant; pM, picomolar. 1. Lacy SE, et al. mAbs. 2015;7(3):605-619; 2. Wang SX, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(12):1952-1961; 3. Bihorel S, et al. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1009-1017; 4. Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT06468228. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06468228. Accessed November 26, 2024; 5. Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT06603077. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06603077. Accessed November 26, 2024. Lutikizumab1,2 AVTX-0093 IL-1β Potential AVTX-009 profile advantages in HS Potential to translate to higher efficacy Potential for less frequent dosing IL-1β IL-1α
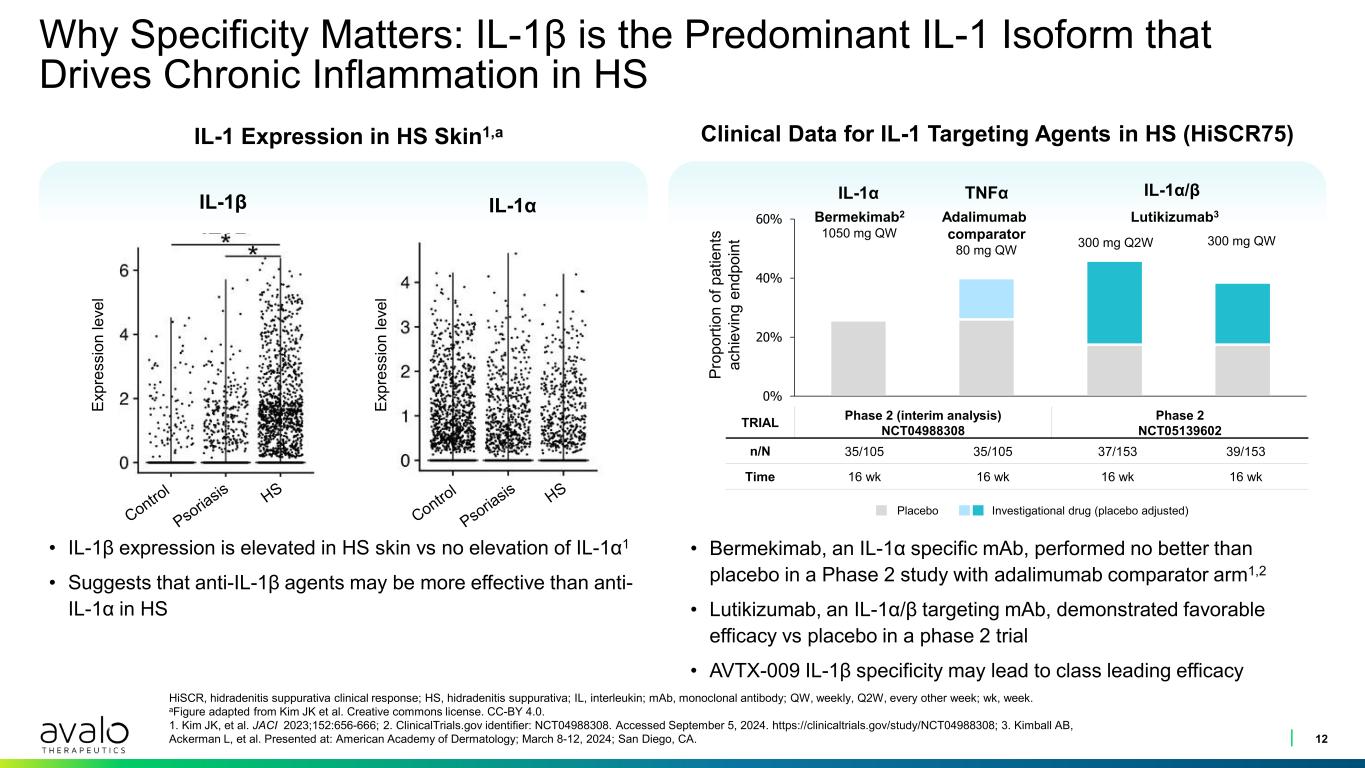
0% 20% 40% 60% Why Specificity Matters: IL-1β is the Predominant IL-1 Isoform that Drives Chronic Inflammation in HS 12 HiSCR, hidradenitis suppurativa clinical response; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; IL, interleukin; mAb, monoclonal antibody; QW, weekly, Q2W, every other week; wk, week. aFigure adapted from Kim JK et al. Creative commons license. CC-BY 4.0. 1. Kim JK, et al. JACI 2023;152:656-666; 2. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04988308. Accessed September 5, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04988308; 3. Kimball AB, Ackerman L, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA. IL-1 Expression in HS Skin1,a • IL-1β expression is elevated in HS skin vs no elevation of IL-1α1 • Suggests that anti-IL-1β agents may be more effective than anti- IL-1α in HS TRIAL Phase 2 (interim analysis) NCT04988308 Phase 2 NCT05139602 n/N 35/105 35/105 37/153 39/153 Time 16 wk 16 wk 16 wk 16 wk Clinical Data for IL-1 Targeting Agents in HS (HiSCR75) IL-1α Bermekimab2 1050 mg QW IL-1α/β Lutikizumab3 300 mg Q2W 300 mg QW TNFα Adalimumab comparator 80 mg QW IL-1β IL-1α • Bermekimab, an IL-1α specific mAb, performed no better than placebo in a Phase 2 study with adalimumab comparator arm1,2 • Lutikizumab, an IL-1α/β targeting mAb, demonstrated favorable efficacy vs placebo in a phase 2 trial • AVTX-009 IL-1β specificity may lead to class leading efficacy Ex pr es si on le ve l Ex pr es si on le ve l Pr op or tio n of p at ie nt s ac hi ev in g en dp oi nt Placebo Investigational drug (placebo adjusted)
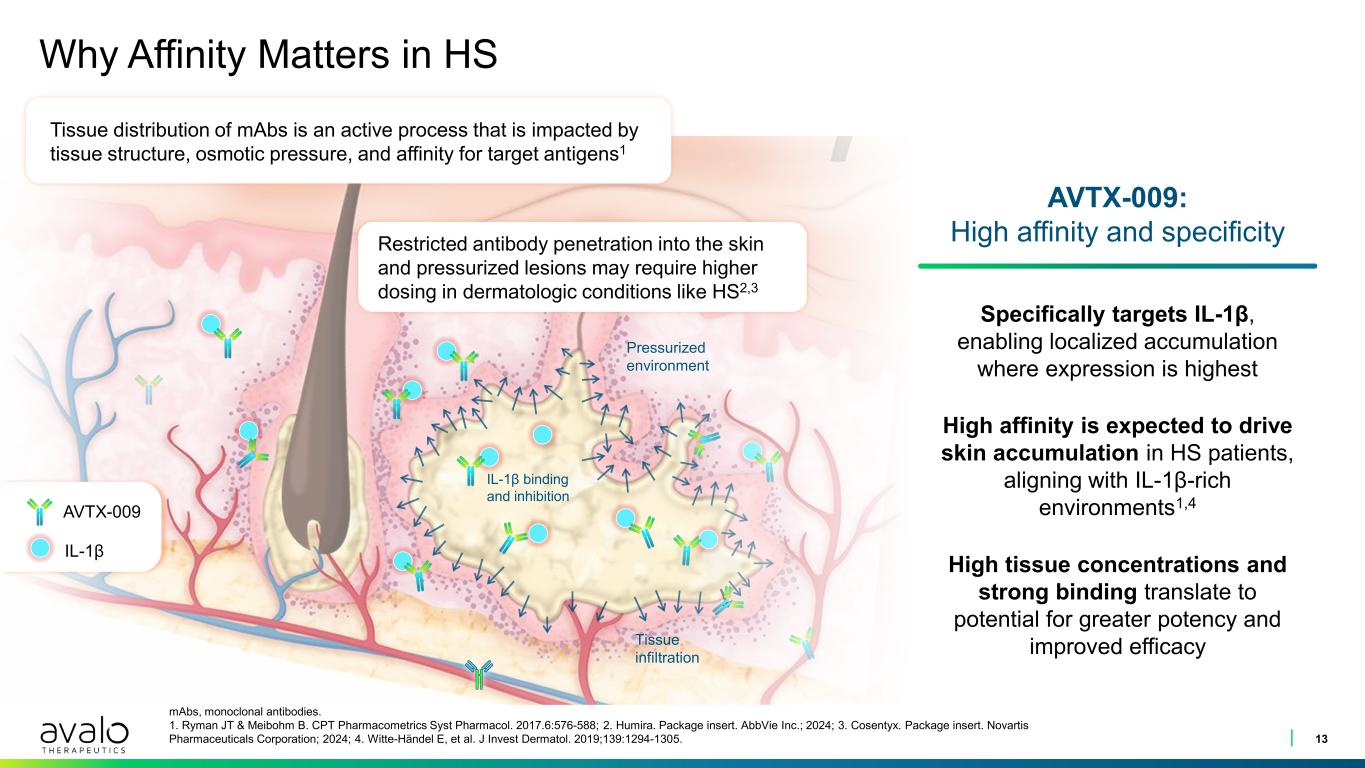
Why Affinity Matters in HS 13 mAbs, monoclonal antibodies. 1. Ryman JT & Meibohm B. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2017.6:576-588; 2. Humira. Package insert. AbbVie Inc.; 2024; 3. Cosentyx. Package insert. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2024; 4. Witte-Händel E, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:1294-1305. IL-1β AVTX-009 Tissue distribution of mAbs is an active process that is impacted by tissue structure, osmotic pressure, and affinity for target antigens1 AVTX-009: High affinity and specificity Specifically targets IL-1β, enabling localized accumulation where expression is highest Restricted antibody penetration into the skin and pressurized lesions may require higher dosing in dermatologic conditions like HS2,3 IL-1β binding and inhibition Pressurized environment Tissue infiltration High affinity is expected to drive skin accumulation in HS patients, aligning with IL-1β-rich environments1,4 High tissue concentrations and strong binding translate to potential for greater potency and improved efficacy
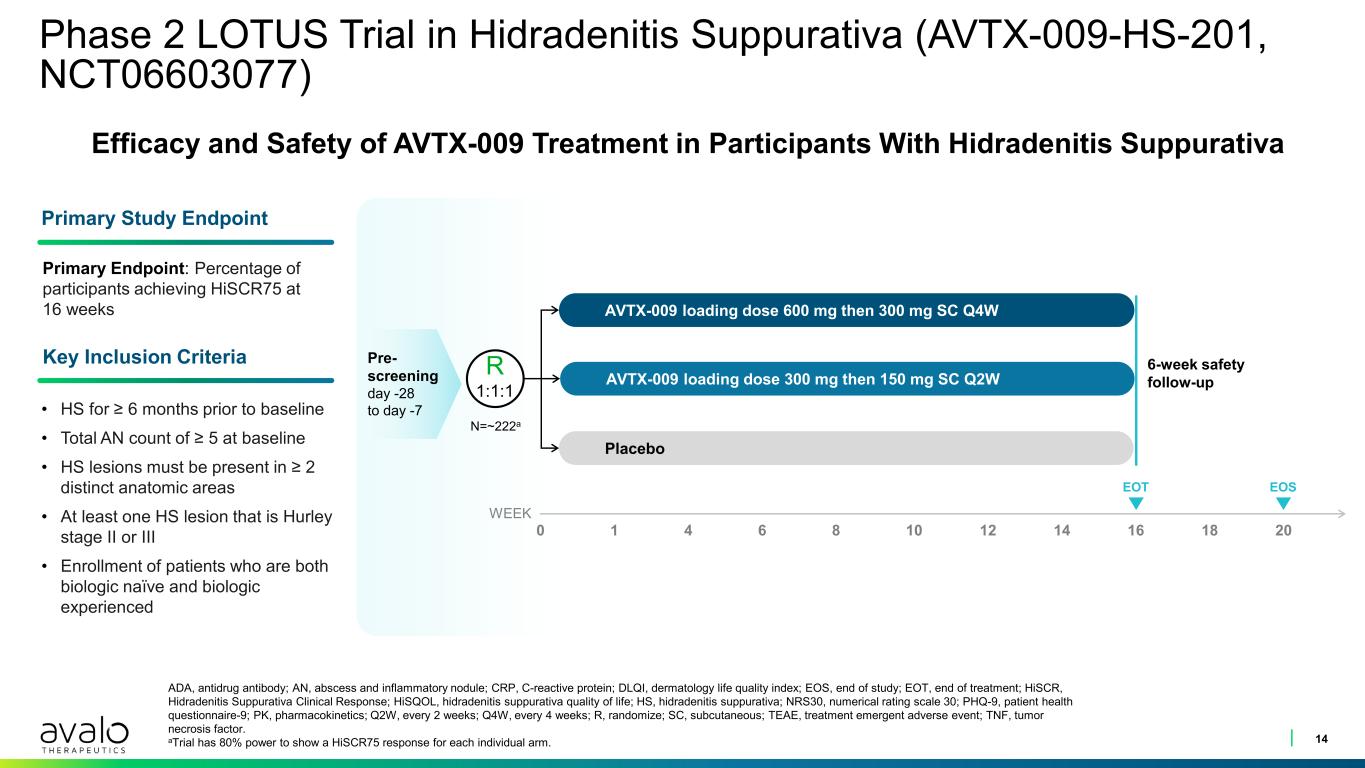
Phase 2 LOTUS Trial in Hidradenitis Suppurativa (AVTX-009-HS-201, NCT06603077) 14 ADA, antidrug antibody; AN, abscess and inflammatory nodule; CRP, C-reactive protein; DLQI, dermatology life quality index; EOS, end of study; EOT, end of treatment; HiSCR, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response; HiSQOL, hidradenitis suppurativa quality of life; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; NRS30, numerical rating scale 30; PHQ-9, patient health questionnaire-9; PK, pharmacokinetics; Q2W, every 2 weeks; Q4W, every 4 weeks; R, randomize; SC, subcutaneous; TEAE, treatment emergent adverse event; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. aTrial has 80% power to show a HiSCR75 response for each individual arm. • HS for ≥ 6 months prior to baseline • Total AN count of ≥ 5 at baseline • HS lesions must be present in ≥ 2 distinct anatomic areas • At least one HS lesion that is Hurley stage II or III • Enrollment of patients who are both biologic naïve and biologic experienced Primary Endpoint: Percentage of participants achieving HiSCR75 at 16 weeks AVTX-009 loading dose 600 mg then 300 mg SC Q4W AVTX-009 loading dose 300 mg then 150 mg SC Q2W Placebo 6-week safety follow-up Pre- screening day -28 to day -7 EOT WEEK Efficacy and Safety of AVTX-009 Treatment in Participants With Hidradenitis Suppurativa Primary Study Endpoint Key Inclusion Criteria R 1:1:1 N=~222a 0 1 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 EOS
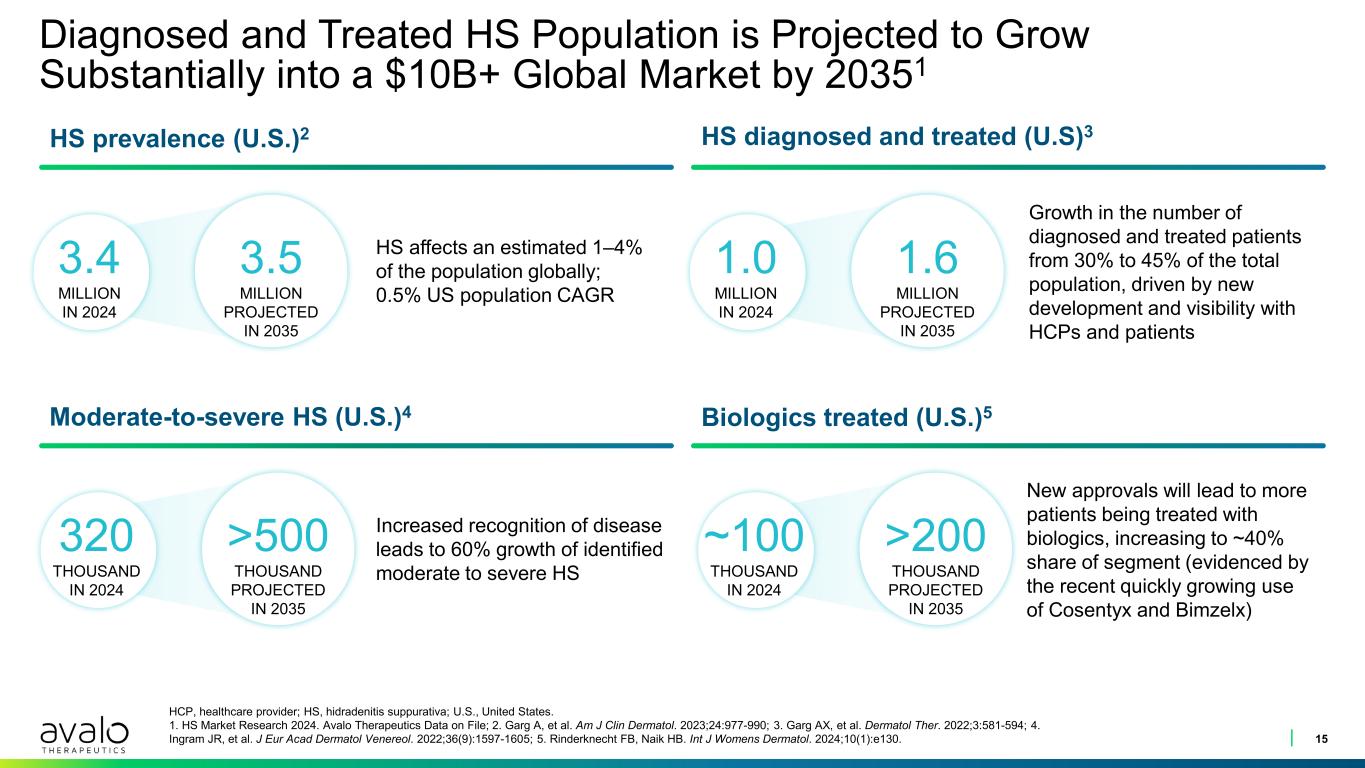
Diagnosed and Treated HS Population is Projected to Grow Substantially into a $10B+ Global Market by 20351 15 HCP, healthcare provider; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; U.S., United States. 1. HS Market Research 2024. Avalo Therapeutics Data on File; 2. Garg A, et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023;24:977-990; 3. Garg AX, et al. Dermatol Ther. 2022;3:581-594; 4. Ingram JR, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(9):1597-1605; 5. Rinderknecht FB, Naik HB. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10(1):e130. HS affects an estimated 1–4% of the population globally; 0.5% US population CAGR 3.4 MILLION IN 2024 3.5 MILLION PROJECTED IN 2035 1.0 MILLION IN 2024 1.6 MILLION PROJECTED IN 2035 ~100 THOUSAND IN 2024 >200 THOUSAND PROJECTED IN 2035 320 THOUSAND IN 2024 >500 THOUSAND PROJECTED IN 2035 HS prevalence (U.S.)2 HS diagnosed and treated (U.S)3 Growth in the number of diagnosed and treated patients from 30% to 45% of the total population, driven by new development and visibility with HCPs and patients Moderate-to-severe HS (U.S.)4 Increased recognition of disease leads to 60% growth of identified moderate to severe HS Biologics treated (U.S.)5 New approvals will lead to more patients being treated with biologics, increasing to ~40% share of segment (evidenced by the recent quickly growing use of Cosentyx and Bimzelx)
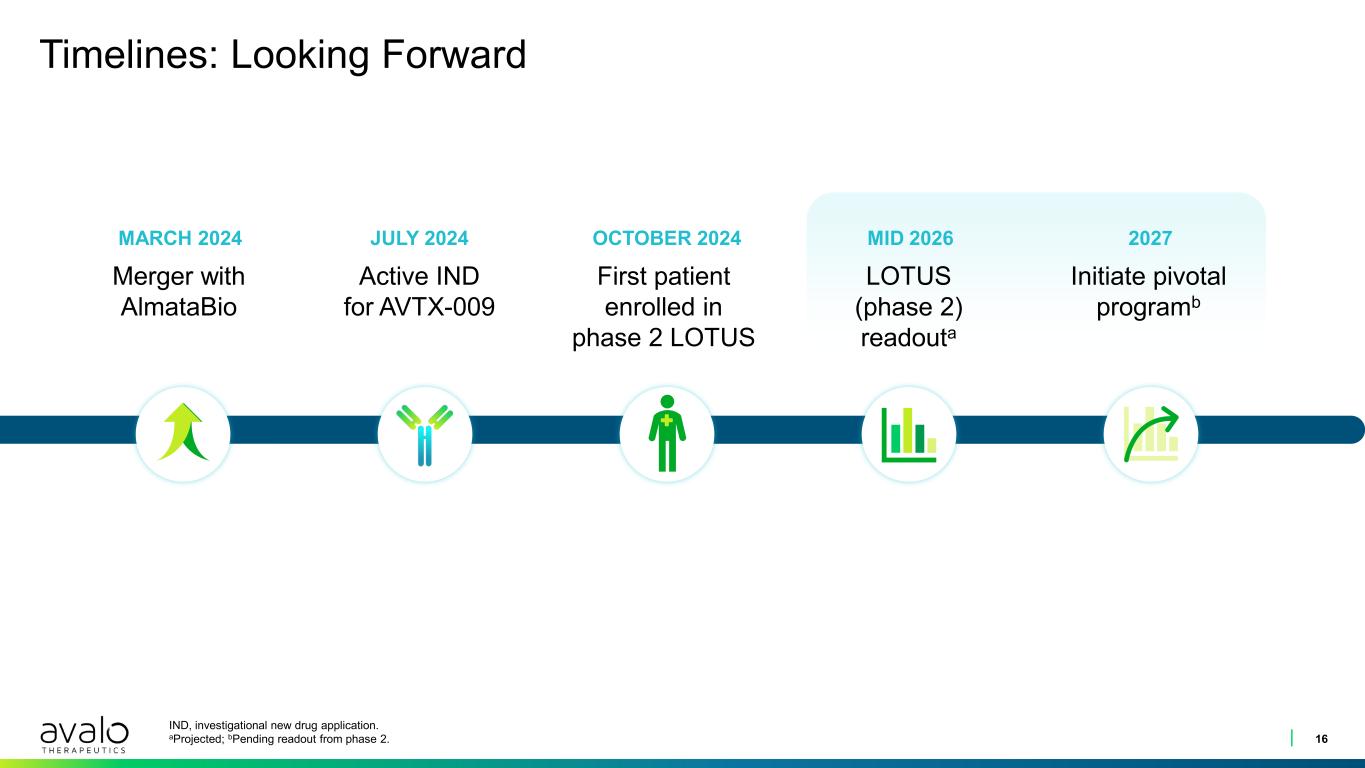
Timelines: Looking Forward 16 IND, investigational new drug application. aProjected; bPending readout from phase 2. MARCH 2024 JULY 2024 OCTOBER 2024 MID 2026 2027 Merger with AlmataBio Active IND for AVTX-009 First patient enrolled in phase 2 LOTUS LOTUS (phase 2) readouta Initiate pivotal programb
Broad Potential for Indication Expansion: Clinical Rationale for IL-1 Targeting Therapies in Additional Disease States 17 CRP, C-reactive protein; CV, cardiovascular; DIRA, deficiency of interleukin receptor 1 antagonist; HS, hidradenitis suppurativa; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; MI, myocardial infarction; OA, osteoarthritis; RA, rheumatoid arthritis. 1. Ilaris. Package insert. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; 2023; 2. Kineret. Package insert. Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB; 3. Schieker, et al. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2020;173(7):509-515; 4. Mao L, et al. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2566; 5. Friedrich M, et al. Nat Med. 2021;27(11):1970-1981; 6. Cader MZ, Kaser A. Nat Med. 2021;27(11):1870-1871; 7. Chen WT, Chi CC. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(9):1022-1027; 8. Zhang M, et al. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(15):3506-3516; 9. Ridker, et al. NEJM . 2017;377(12):1119-1131; 10. Arcalyst. Package insert. Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals (UK), Ltd.; 2021. • IL-1β is upregulated in inflammasome activation in Crohn’s disease4 – IL-1 activity may define a non-responder subset to current therapies5,6 – Observed overlap of patients that have IBD and HS7,8 • Like in HS, current advanced therapies for IBD often fail to deliver adequate response • IL-1 targeting therapies approved in RA and acute gout flare1,2 • CANTOS study (Novartis): IL-1β blockage with canakinumab reduced total joint replacements in OA patients with high CRP3 • Mechanistic rationale extends to other crystal-induced arthritis (e.g., CPPD) • While not a current focus for Avalo, IL-1 targeting therapies approved in rare autoinflammatory diseases (e.g., periodic fevers, DIRA, Still’s disease and recurrent pericarditis)1,2,10 • CANTOS study (Novartis): canakinumab reduced major CV events in patients with prior MI and elevated CRP9 • Additional indications with supporting mechanistic and clinical rationales Arthritis Indications Inflammatory Bowel Disease Additional Indications with Established Clinical Proof of Concept Avalo is currently assessing additional immunology indications for investment
Avalo Summary (NASDAQ: AVTX) 18 IL, interleukin; mAB, monoclonal antibody. 1.Dinarello CA. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):8-27; 2. Bihorel S, et al. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1009-1017; 3. Lacy SE, et al. mAbs. 2015;7(3):605-619; 2. Wang SX, et al. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(12):1952-1961; 4. Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT06468228. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06468228. Accessed November 26, 2024; 5. Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT06603077. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06603077. Accessed November 26, 2024.; 5. HS Market Research 2024. OUR APPROACH: Next generation therapies targeting IL-1β, a master regulator of inflammation1 LEAD ASSET AVTX-009: A high-affinity, IL-1β–specific mAb2 Differentiated Profile: 15x higher affinity and longer half-life than lutikizumab; potential for best-in-class and best-in-disease profile with potential increased efficacy and less frequent dosing2-5 Lead Indication – Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS): Projected to become a $10B+ market by 20355 driven by growth in diagnosis and treatment + high patient need due to incomplete response rates for available anti-TNF and anti-IL-17 therapies Clinical Momentum: Phase 2 LOTUS trial in HS is enrolling; topline data expected mid-2026 Broad Potential: Scientific and clinical rationale for expansion into additional IL-1β–driven diseases Strong Financial Foundation: Expected cash runway into 2028

NASDAQ: AVTX www.avalotx.com 19

Appendix 20

Key Financial Metrics 21 1. Does not include 5.3M of stock options, restricted stock units and performance stock units outstanding resulting in a fully dilutive share count of 42.5M as of September 30, 2025, 2. Cash, cash equivalents and short- term investments, common shares outstanding, and preferred shares outstanding as of September 30, 2025 are preliminary, unaudited and subject to change Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of approximately $112 million as of September 30, 20252, provides expected runway into 2028 As of September 30, 2025 Number of Shares Common stock Common shares outstanding1,2 17.8M Assuming conversion of preferred stock Preferred stock2 19.4M Adjusted share count Adjusted common shares outstanding1,2 37.2M Adjusted market capitalization Stock price $12.71 Adjusted market capitalization $472.7M