
1 Avalo Therapeutics, Inc. (AVTX) Corporate Presentation September 2024 Exhibit 99.1

2 This presentation may include forward-looking statements made pursuant to the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward- looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. Such forward-looking statements are subject to significant risks and uncertainties that are subject to change based on various factors (many of which are beyond Avalo’s control), which could cause actual results to differ from the forward-looking statements. Such statements may include, without limitation, statements with respect to Avalo’s plans, objectives, projections, expectations and intentions and other statements identified by words such as “projects,” “may,” “might,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “continue,” “seeks,” “aims,” “predicts,” “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “intends,” “plans,” “potential,” or similar expressions (including their use in the negative), or by discussions of future matters such as: integration of AVTX-009 into our operations; drug development costs, timing of trial results and other risks, including reliance on investigators and enrollment of patients in clinical trials; the intended use of the proceeds from the private placement; reliance on key personnel; regulatory risks; general economic and market risks and uncertainties, including those caused the war in Ukraine and the Middle East; and those other risks detailed in Avalo’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, available at www.sec.gov. Actual results may differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. Except as required by applicable law, Avalo expressly disclaims any obligations or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in Avalo’s expectations with respect thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any statement is based. Forward-Looking Statements

3 • Potential for a Best-in-Disease Profile in HS – High potency and favorable half-life may allow for improved efficacy and convenient dosing – Potential in other autoimmune diseases • Key Clinical Evidence Supporting IL-1β in HS – In a large, well controlled Phase 2 trial (NCT05139602), lutikizumab validates IL-1β targeting in HS. Efficacy was comparable with other HS therapies despite a more severe patient population1 – Clinical evidence suggests anti-IL-1α therapy is not effective in HS2,3 – MAS825 (IL-1β/IL-18 bispecific) showed positive results in a Phase 2 randomized controlled study (NCT03827798)4 – Monospecific IL-1b inhibition may outperform bispecifics that address targets that are unvalidated (IL-18) or known not to contribute to efficacy (IL-1a) • HS Anticipated to Become Multi-Billion Dollar Market • IND is active permitting initiation of Phase 2 LOTUS Trial • First Patient Enrolled in Phase 2 LOTUS Trial Expected 2H 2024 • Expected Cash Runway into 2027 Executive Summary and AVTX-009 Development Timeline 1. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA 2. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04988308. Updated November 13, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 NCT04019041 3. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04019041. Updated July 27, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 :// 4. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA

4 Garry A. Neil, MD Chief Executive Officer Chairman of the Board Lisa Hegg, PhD SVP, Program Management, Corporate Infrastructure, Clinical Operations Colleen Matkowski SVP, Global Regulatory Affairs, Quality Assurance Dino C. Miano, PhD SVP, CMC, Technical Operations Chris Sullivan Chief Financial Officer Experienced Management Team Decades of successful leadership, product development, and commercialization in pharma and biotech Mittie Doyle, MD Chief Medical Officer Paul Varki Chief Legal Officer

5 • High-affinity humanized antibody that potently neutralizes IL-1β – Originally developed by Lilly – Exceptional Kd of <3 pM (picomolar) Superior potency vs ILARIS in vitro – t1/2 ~19 days (SC and IV) – Bioavailability ~73% • Clinical experience: 245 patients studied in Phase 1 & Phase 2 trials3 – Excellent tolerability and safety at all doses up to 180 mg weekly – Marked lowering of hs-CRP after a single dose – Potency and half life expected to support Q4W or less frequent dosing in HS • Suitable for subcutaneous and intravenous formulation – Stable 150 mg/ml dosage form – Plan for commercial presentation to be an autoinjector AVTX-009 Highly Potent and Specific Inhibitor of a Validated Immune Target; Potential for Q2W to Q12W Dosing 1,2 AVTX-009 has Strong Pharmacokinetic Profile AVTX-009 1. Data on file 2. Bihorel S, et al. AAPS J. 2014;16(5):1009-1017 3. Sloan-Lancaster J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(8):2239-2246 AVTX-009 has Higher Potency than Canakinumab and Gevokizumab M ea n A V TX -0 09 S er um C on ce nt ra tio n ug /m L
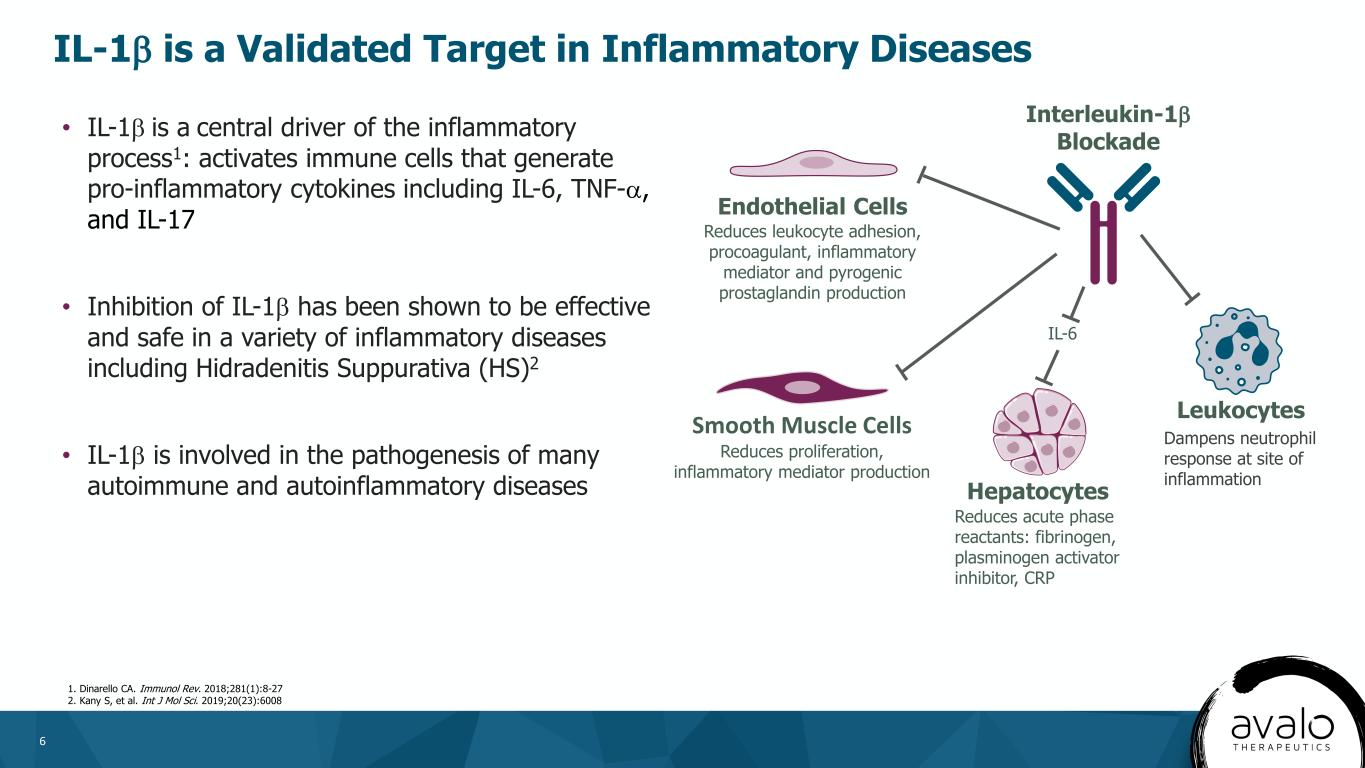
6 • IL-1β is a central driver of the inflammatory process1: activates immune cells that generate pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 • Inhibition of IL-1β has been shown to be effective and safe in a variety of inflammatory diseases including Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)2 • IL-1β is involved in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases Interleukin-1β Blockade Endothelial Cells Reduces leukocyte adhesion, procoagulant, inflammatory mediator and pyrogenic prostaglandin production Smooth Muscle Cells Reduces proliferation, inflammatory mediator production Hepatocytes Reduces acute phase reactants: fibrinogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor, CRP Leukocytes IL-6 1. Dinarello CA. Immunol Rev. 2018;281(1):8-27 2. Kany S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6008 IL-1β is a Validated Target in Inflammatory Diseases Dampens neutrophil response at site of inflammation

7 Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS)
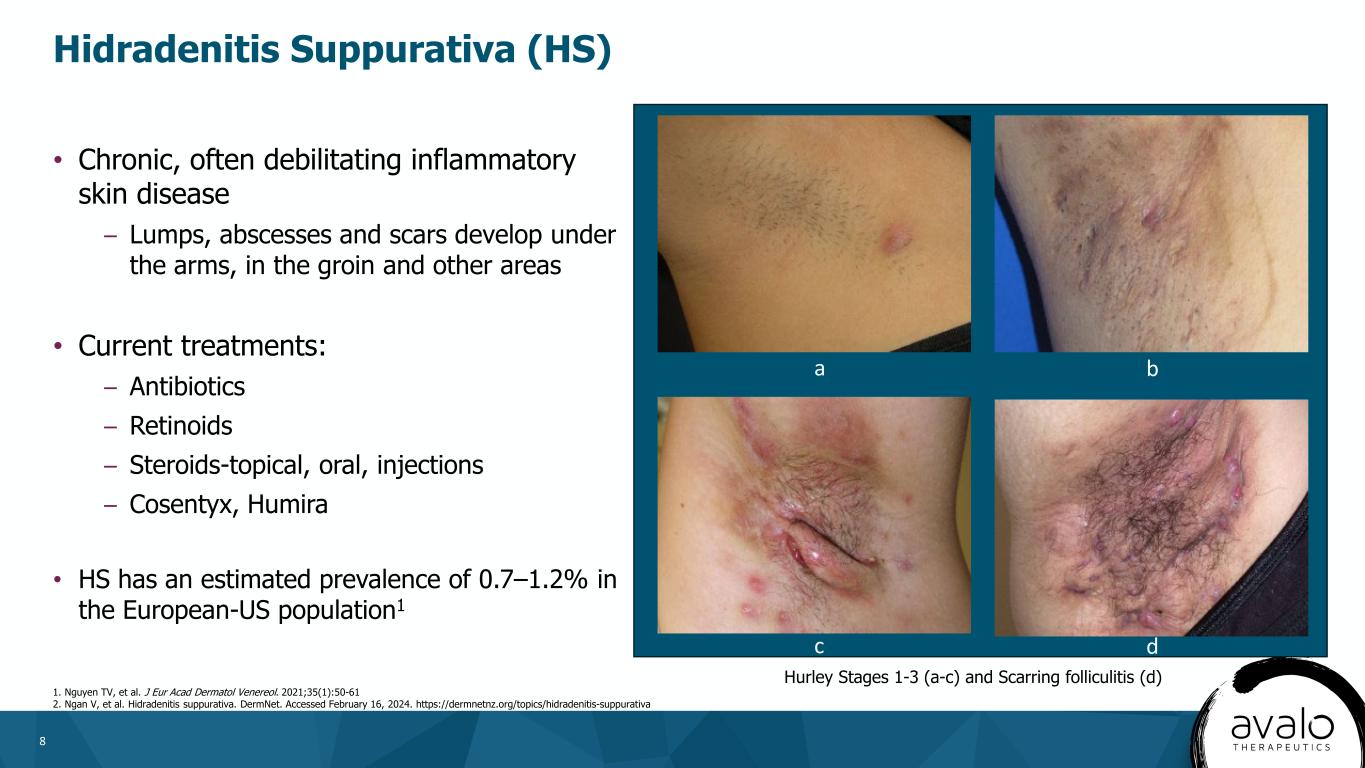
8 • Chronic, often debilitating inflammatory skin disease – Lumps, abscesses and scars develop under the arms, in the groin and other areas • Current treatments: – Antibiotics – Retinoids – Steroids-topical, oral, injections – Cosentyx, Humira • HS has an estimated prevalence of 0.7–1.2% in the European-US population1 Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) 1. Nguyen TV, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35(1):50-61 2. Ngan V, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa. DermNet. Accessed February 16, 2024. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/hidradenitis-suppurativa Hurley Stages 1-3 (a-c) and Scarring folliculitis (d) c d a b

9 • Inflammatory cascade in HS is triggered by various external stimuli – Smoking, dysbiosis, or mechanical stress • IL-1β is a key driver of the inflammatory cascade that leads to the destruction of the pilosebaceous unit – Increased IL-1β levels in lesional skin2,3 – Genetic associations4 – Clinical benefit has been observed with anti-IL-1 drugs IL-1β is Strongly Implicated in the Pathophysiology of HS1 1. Calabrese L, et al. Biomolecules. 2024;14(2):175 2. Vossen ARJV, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(7):1463-1466.e2 3. Kelly G, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(6):1431-1439 4. Marzano AV, et al. Dermatology. 2022;238(5):860-869 DAMPs, damage-associated molecular pattern molecules; DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; IL-R, interleukin receptor; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules.

10 Baseline Patient Characteristics of Biologics from Recent HS Trials Lutik izumab Trial Enrolled More Severe Patients than Competitor Trials 1. Kimball AB et al. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375:422-34; 2. Kimball AB et al. Lancet. 2023; 401:747-7613; 3. Presentations at American Academy of Dermatology (AAD 2023), March 17-21 New Orleans, LA and 2023 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV 2023), October 11-14, Berlin, Germany 4. R&D Presentation – Results MIRA trial June 26th 2023 https://ir.moonlaketx.com/static-files/86c71a51-5836-4f1c-9a2c-45e440a50d75 5. Kimball AB et al. presentation at American Academy of Dermatology (AAD 2024), 8-12 March 2024, San Diego, CA Patient Characteristics adalimumab PIONEER I / II1 secukinumab SUNSHINE / SUNRISE2 bimekizumab BE HEARD I / II3 sonelokimab MIRA4 lutikizumab NCT051396025 Age (years), mean 34.9 – 37.8 35.5 – 37.3 36.7 / 36.6 37.6 37.0-39.5 Gender, female, % 59.5 – 69.3 54 – 57 63.0 / 50.7 59.8 53.8-67.6 Race, White, % 75.8 – 87.7 74 – 81 77.8 / 81.5 85.0 64.9-88.9 BMI, kg/m2, mean 31.3 – 34.5 31.4 – 32.8 33.8 / 32.3 33.7 33.0-34.1 Smoking, current, % 52.9 – 67.3 50 – 58 43.0 / 48.1 46.6 24.3-46.2 Duration of HS years, mean 8.8 – 9.9 6.6 – 8.2 9.0 / 7.0 8.5 10.0-13.2 Lesions, mean - AN count - DT 10.7 – 14.4 3.0 – 4.6 12.6 – 13.9 3.2 – 3.6 16 / 16.5 3.8 / 3.4 14.0 3.5 11.4-17.0 5.7-8.7 Hurley stage, % - I - II - III 0 52.3 – 54.6 45.4 – 47.7 2 – 6 51 – 60 28 – 46 0 50.3 / 61.1 49.7 / 38.9 0 63.7 36.3 25.6-35.1 64.9-74.4 Prior biologic use, % 0 20 - 26 25.0 / 13.2 17.5 100 TNF failure entry criteria

11 Lutikizumab Efficacy Comparable to Other Agents in a More Severe Patient Population that Failed TNF-α Therapy1 HiSCR75 Lower response rates observed in patients that have been previously treated with biologic agents or Hurley Stage 32-4 1. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA 2. Kimball AB, et al. Supplement. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(5):422-434 3. Sayed, et al. Poster presented at: European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress; October 11-14, 2023. Berlin, Germany 4. Zouboulis CC, et al. Br J Dermatol. Published online March 12, 2024. doi:10.1093/bjd/ljae098 HiSCR50
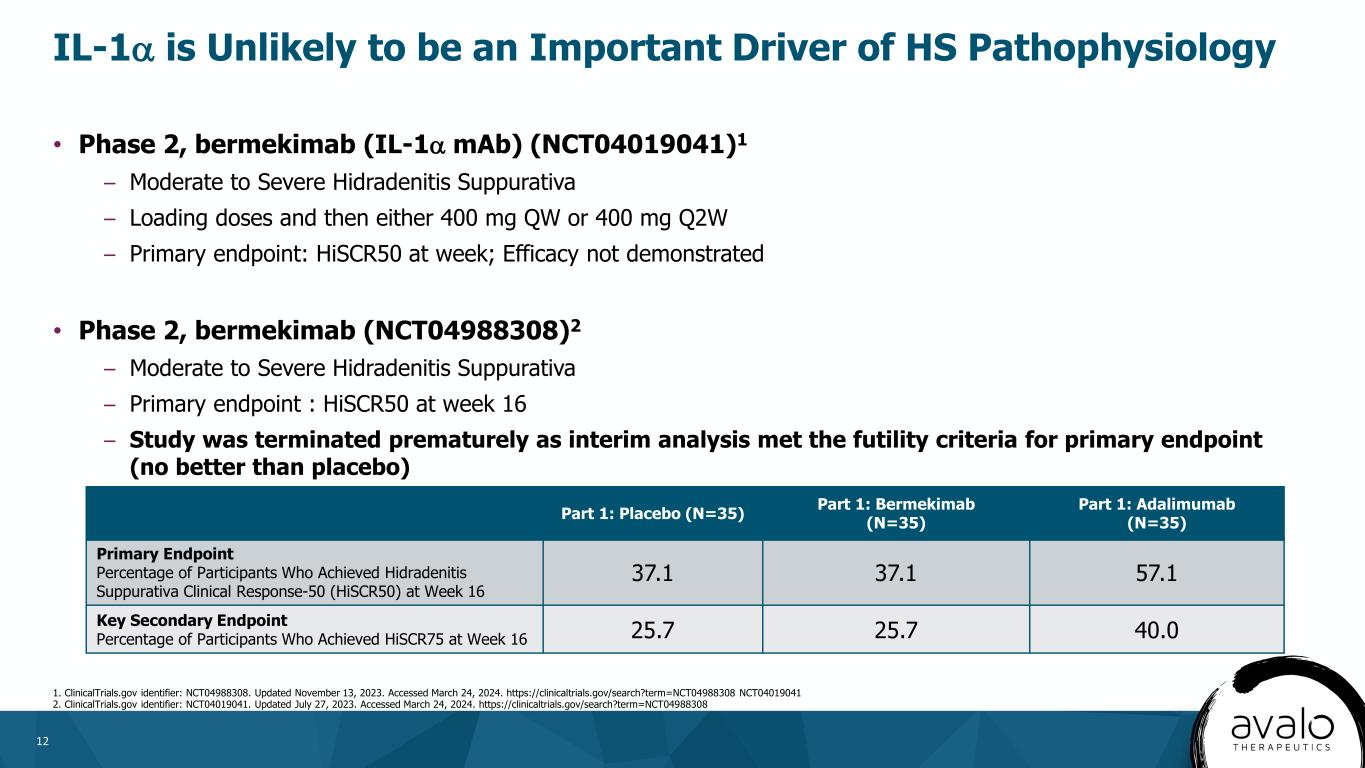
12 • Phase 2, bermekimab (IL-1α mAb) (NCT04019041)1 – Moderate to Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa – Loading doses and then either 400 mg QW or 400 mg Q2W – Primary endpoint: HiSCR50 at week; Efficacy not demonstrated • Phase 2, bermekimab (NCT04988308)2 – Moderate to Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa – Primary endpoint : HiSCR50 at week 16 – Study was terminated prematurely as interim analysis met the futility criteria for primary endpoint (no better than placebo) IL-1α is Unlikely to be an Important Driver of HS Pathophysiology https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 1. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04988308. Updated November 13, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 NCT04019041 2. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04019041. Updated July 27, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 :// Part 1: Placebo (N=35) Part 1: Bermekimab (N=35) Part 1: Adalimumab (N=35) Primary Endpoint Percentage of Participants Who Achieved Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response-50 (HiSCR50) at Week 16 37.1 37.1 57.1 Key Secondary Endpoint Percentage of Participants Who Achieved HiSCR75 at Week 16 25.7 25.7 40.0
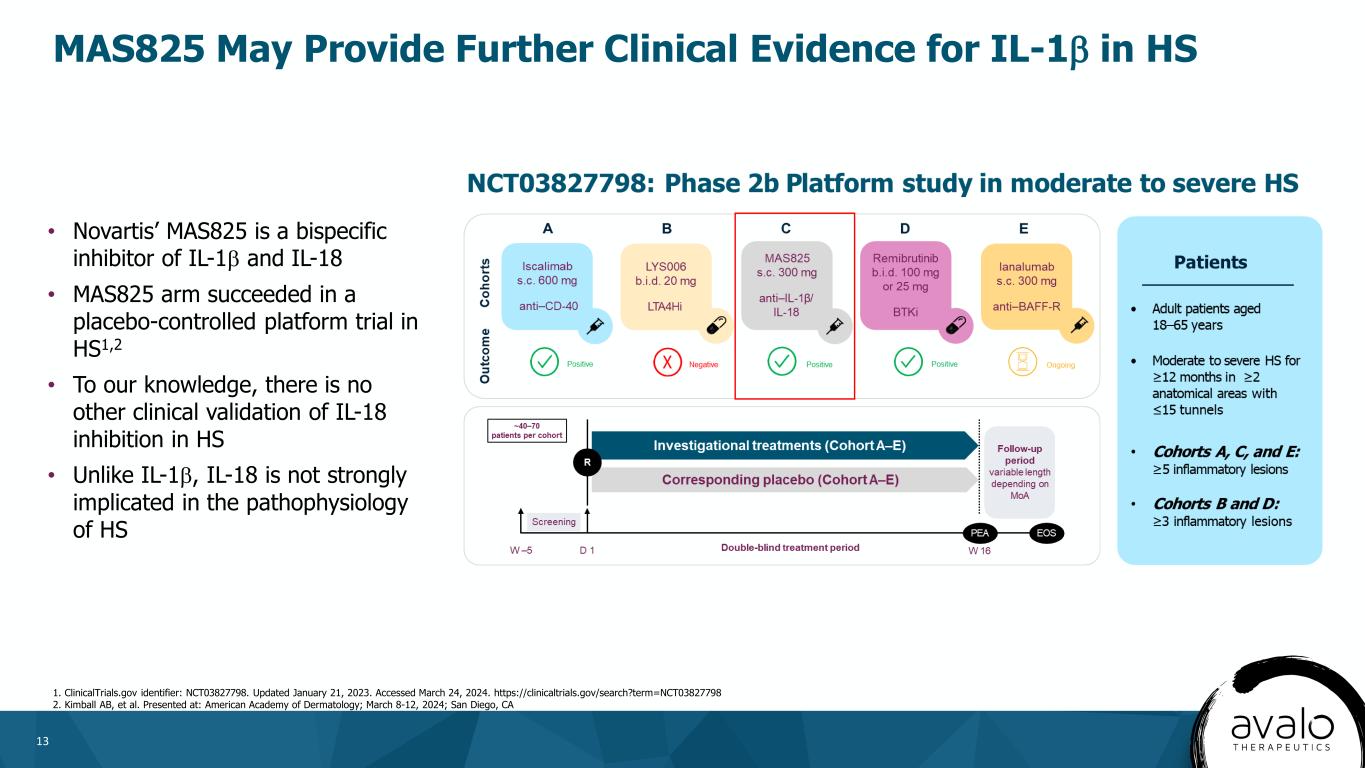
13 MAS825 May Provide Further Clinical Evidence for IL-1β in HS 1. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03827798. Updated January 21, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT03827798 2. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA • Novartis’ MAS825 is a bispecific inhibitor of IL-1β and IL-18 • MAS825 arm succeeded in a placebo-controlled platform trial in HS1,2 • To our knowledge, there is no other clinical validation of IL-18 inhibition in HS • Unlike IL-1β, IL-18 is not strongly implicated in the pathophysiology of HS

14 A third of moderate to severe HS patients, or over 100,000 patients, are treated with biologics *Independent Market Analysis by Biotech Value Advisors LLC Over 3 million people in the US have hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) An estimated 1% of US population or 3.34 million people suffer with HS in the United States Est. 320,000 have moderate-to-severe disease 32% of those HS patients diagnosed and treated population have moderate-to-severe disease, amounting to approximately 320,000 patients Over 100,000 patients treated w/biologics Potential Addressable Markets Approximately 1 million people, or 0.3% of US population, are diagnosed with and treated for HS As many as 1 million people in the US with HS are diagnosed and treated Large Unmet Need in HS Global HS market has $9.5B+ sales potential*, w ith AVTX-009 best-in-class potential
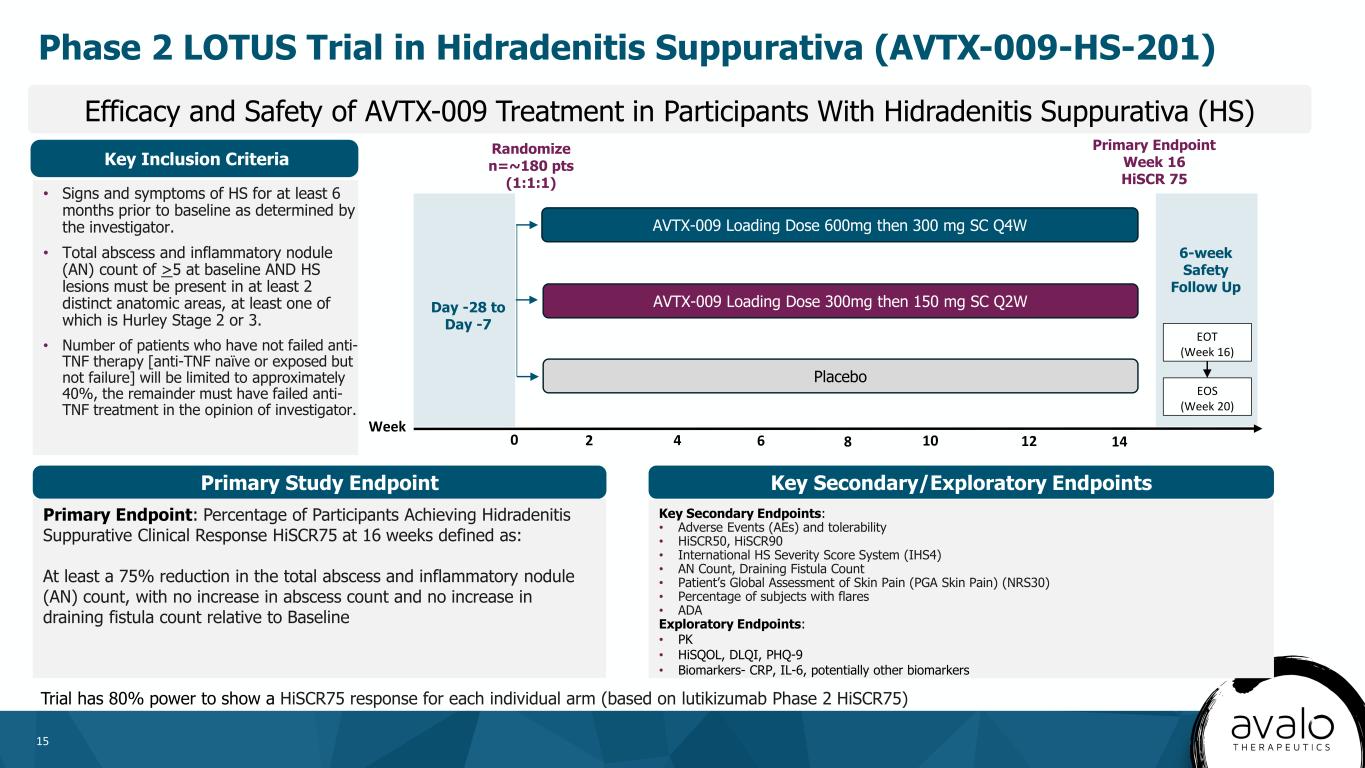
15 Key Secondary/Exploratory Endpoints Efficacy and Safety of AVTX-009 Treatment in Participants With Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) Key Secondary Endpoints: • Adverse Events (AEs) and tolerability • HiSCR50, HiSCR90 • International HS Severity Score System (IHS4) • AN Count, Draining Fistula Count • Patient’s Global Assessment of Skin Pain (PGA Skin Pain) (NRS30) • Percentage of subjects with flares • ADA Exploratory Endpoints: • PK • HiSQOL, DLQI, PHQ-9 • Biomarkers- CRP, IL-6, potentially other biomarkers • Signs and symptoms of HS for at least 6 months prior to baseline as determined by the investigator. • Total abscess and inflammatory nodule (AN) count of >5 at baseline AND HS lesions must be present in at least 2 distinct anatomic areas, at least one of which is Hurley Stage 2 or 3. • Number of patients who have not failed anti- TNF therapy [anti-TNF naïve or exposed but not failure] will be limited to approximately 40%, the remainder must have failed anti- TNF treatment in the opinion of investigator. Key Inclusion Criteria Primary Study Endpoint Primary Endpoint: Percentage of Participants Achieving Hidradenitis Suppurative Clinical Response HiSCR75 at 16 weeks defined as: At least a 75% reduction in the total abscess and inflammatory nodule (AN) count, with no increase in abscess count and no increase in draining fistula count relative to Baseline Phase 2 LOTUS Trial in Hidradenitis Suppurativa (AVTX-009-HS-201) Randomize n=~180 pts (1:1:1) AVTX-009 Loading Dose 600mg then 300 mg SC Q4W AVTX-009 Loading Dose 300mg then 150 mg SC Q2W Placebo 6-week Safety Follow Up 0 2 4 8 10 12 14 Day -28 to Day -7 EOT (Week 16) EOS (Week 20) Week 6 Primary Endpoint Week 16 HiSCR 75 Trial has 80% power to show a HiSCR75 response for each individual arm (based on lutikizumab Phase 2 HiSCR75)

16 Potential Additional Indications

17 • IL-1β plays a central role in inflammation in IBD1 – IL-1β being a key cytokine produced upon inflammasome activation – Dysregulated inflammasome activation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s Disease (CD) • IL-1-driven stromal–neutrophil interactions define a subset of patients that do not respond to current therapies 2,3 • Observed overlap of patients that have IBD and HS4,5 Role of IL-1β in IBD ://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02566 1. Mao L, et al. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2566 2. Friedrich M, et al. Nat Med. 2021;27(11):1970-1981 3. Cader MZ, Kaser A. Nat Med. 2021;27(11):1870-1871 4. Chen WT, Chi CC. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155(9):1022-1027 5. Zhang M, et al. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(15):3506-3516

18 • The goal of IBD therapeutics is remission – Only a minority of IBD patients obtain remission with current therapies • AbbVie plans to evaluate lutikizumab, dual-variable-domain interleukin (IL) 1α/1β antagonist as monotherapy in UC and in combination with SKYRIZI in Crohn’s – “…we believe lutikizumab has the potential to be used in combinations to provide transformational levels of efficacy in IBD. We plan to evaluate combo approaches with lutikizumab and Skyrizi… in Crohn's. Our Phase 2 studies in IBD are expected to begin later this year.”--Roopal Thakkar, Senior Vice President, Chief Medical Officer, Global Therapeutics --from AbbVie 4Q23 Earnings Call Transcript • There is an opportunity for greater efficacy for patients with IBD with anti-IL-1β as a monotherapy and in combination Recent IL-1 Trial Initiations in IBD

19 Executive Summary

20 • Potential for a Best-in-Disease Profile in HS – High potency and favorable half-life may allow for improved efficacy and convenient dosing – Potential in other autoimmune diseases • Key Clinical Evidence Supporting IL-1β in HS – In a large, well controlled Phase 2 trial (NCT05139602), lutikizumab validates IL-1β targeting in HS. Efficacy was comparable with other HS therapies despite a more severe patient population1 – Clinical evidence suggests anti-IL-1α therapy is not effective in HS2,3 – MAS825 (IL-1β/IL-18 bispecific) showed positive results in a Phase 2 randomized controlled study (NCT03827798)4 – Monospecific IL-1b inhibition may outperform bispecifics that address targets that are unvalidated (IL-18) or known not to contribute to efficacy (IL-1a) • HS Anticipated to Become Multi-Billion Dollar Market • IND is active permitting initiation of Phase 2 LOTUS Trial • First Patient Enrolled in Phase 2 LOTUS Trial Expected 2H 2024 • Expected Cash Runway into 2027 Executive Summary and AVTX-009 Development Timeline 1. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA 2. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04988308. Updated November 13, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 NCT04019041 3. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04019041. Updated July 27, 2023. Accessed March 24, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?term=NCT04988308 :// 4. Kimball AB, et al. Presented at: American Academy of Dermatology; March 8-12, 2024; San Diego, CA

21 Appendix

22 Financial & Investor Information 1 As of August 13, 2024, Avalo has 9.7M shares of common stock outstanding. On August 13, 2024, upon stockholder approval and subject to certain beneficial ownership limitations, Avalo issued 8.7M shares of common stock pursuant to the automatic conversion of 8,648 shares of non-voting Series C convertible preferred stock. NASDAQ: AVTX The following data as of June 30, 2024 • Cash and cash equivalents – $93.4M • Expected cash runway into 2027 • Outstanding common stock – 1.0M1 • Fully diluted shares – 35.5M

23 NASDAQ:AVTX www.avalotx.com